
What is the problem?
In September, russia cynically struck the dam of the Karachunivka Reservoir in Kryvyi Rih. It caused the flooding of more than hundreds of houses. Ukrainian services had to quickly overcome the accident consequences to prevent worse situations and even more significant water losses. Later, the water in the Inhulets River turned red. This immensely confused the townspeople.

But these were only external consequences. First, sometime after the attack, some of the townspeople, whose homes were supplied with water from the reservoir, didn't have access to this resource. And this is half the city.
Second, the critical water level rise led to the flooding of the territories of settlements located downstream of the Inhulets River, along with basements, cellars, and cesspools, significantly worsening the epidemiological situation in the city. People didn't know whether they could use water from the river and wells.
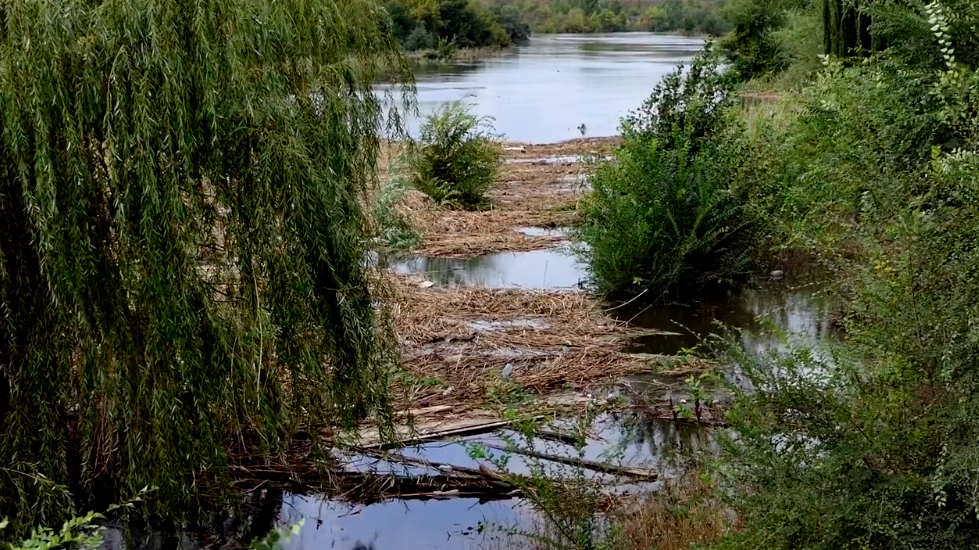
Third, flooding the shores and yards, the water swept away branches, trees, and household garbage. In some locations, they formed islands. Now the channel needs to be cleaned, which has already been done, judging by messages on social media. Such "garbage" islands stop or block the river's flow, negatively affecting it.
What is the solution?
Local environmental monitoring organization conducted a water analysis
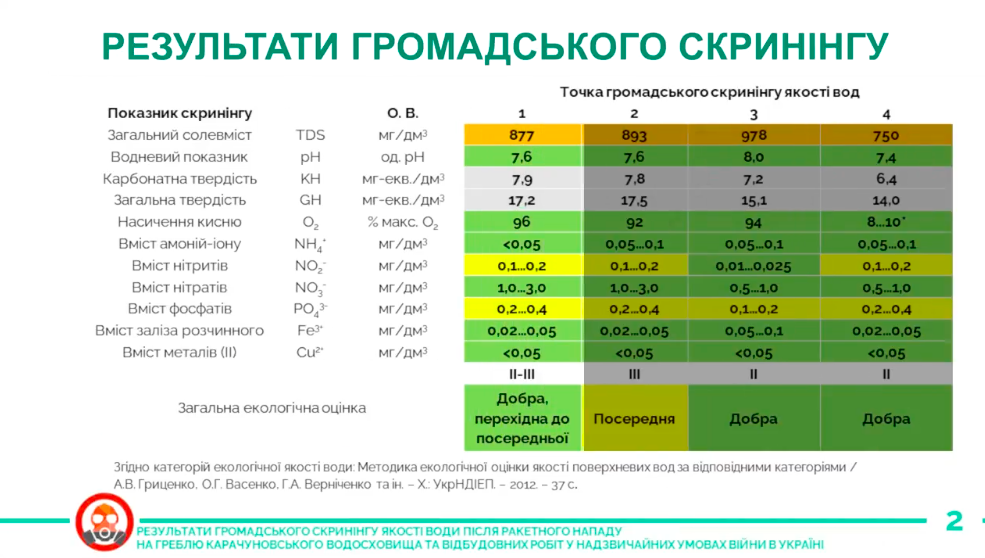
After the accident, the team of the Enough Poisoning Kryvyi Rih public organization took water samples and conducted ecological testing. This is the best way to determine whether the water from the river is safe to use and whether the groundwater in the region will remain safe.
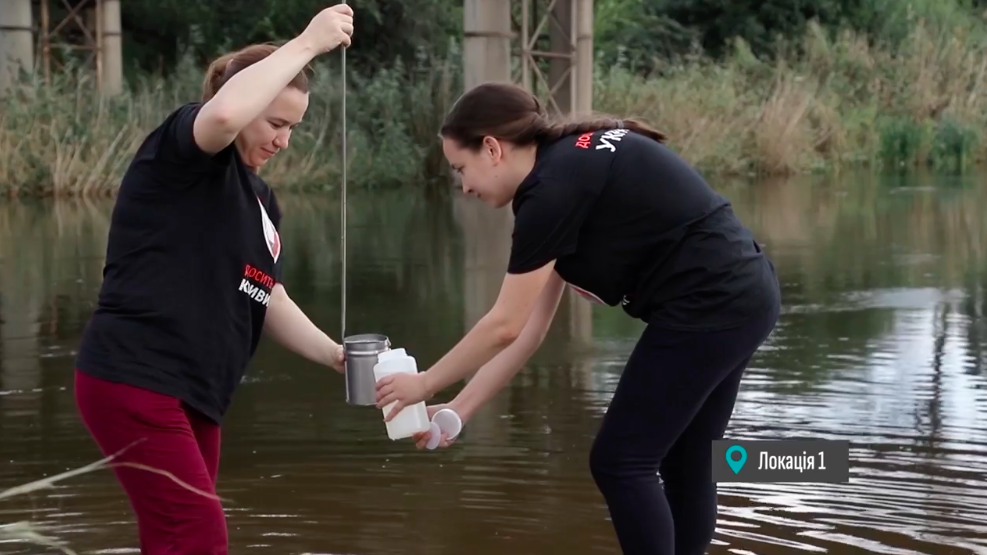

Screenshot from the video by the NGO Enough Poisoning Kryvyi Rih
Tests showed that there is generally no reason to panic. According to the classification, water in all samples belongs to II and III categories: good and mediocre. There are seven categories in total. Waters belonging to categories starting with the 5th are considered dangerous.
Screenshot from the video by the NGO Enough Poisoning Kryvyi Rih
So, the water in the Inhulets River can be called relatively safe. At the same time, some indicators are elevated, although they are within normal limits. Another thing perplexed ecologists: such an accident exposed other environmental problems in the city.
In particular, some increase in the content of phosphates and nitrates in water detected in samples belonging to the III category can be caused by the flooding of engineering networks and cesspools in the yards. Phosphates, for example, can lead to excessive growth of blue-green algae or, as people say, water bloom. And this, in the long run, reduces the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water and negatively affects river inhabitants.
However, the analysis showed that the saturation in all samples was higher than 90%. This means that there will be no oxygen starvation among fish and river vegetation. Therefore, the river inhabitants will not die because of the reddening of the water. No heavy metals were found in the water, and what confused people the most was the red color of the river, which is particles of loam and hematite that will settle to the bottom. By now, the color of the river has already returned to normal.

But we should not relax too early. The head of the Enough Poisoning Kryvyi Rih public organization, in a conversation with Rubryka, stressed that the analysis of sanitary and epidemiological indicators was not carried out, so the public organization cannot fully assess the safety and quality of water.

Screenshot from the video by the NGO Enough Poisoning Kryvyi Rih
What lessons have we learned after the Inhulets River accident?
The trouble happened not only due to the reddening of the river and flooding. The water released from the reservoir carried a lot of garbage from the coastal areas, lying there for years. Also, the current washed away the uncleared thickets of reeds in piles, which dramatically complicated water flow.
👉🏻 Therefore, the organization emphasizes that reeds must occasionally be partially removed in rivers subject to anthropogenic influence. In general, cleaning riverbeds is necessary, and the local government should deal with it.

Screenshot from the video by the NGO Enough Poisoning Kryvyi Rih
The river's flooding after the dam explosion demonstrated another problem—non-compliance with water protection zones around reservoirs. For the Inhulets River, it is 50 m. You cannot build or place other objects here. And if a certain number of houses were erected near Inhulets long before the adoption of these norms, in other places, developers simply neglected them: construction is underway in protected areas of reservoirs, and sometimes even production facilities are located there.
👉🏻 So, we have to conclude: construction standards around reservoirs do not exist by chance: the safety of water quality for the population depends on their observance. Therefore, it is necessary to consider construction legislation in post-war reconstruction and not repeat old mistakes.
Find out about war quality in rivers from local authorities
- If you notice leaks or discharges into the river, pond, or other bodies of water, you can contact Ukraine's State Environmental Inspectorate (SEI). SEI has the right to conduct investigations of leaks and take measures to eliminate the violation if it has occurred.
- For the SEI to conduct such a study, it is necessary to send completed application forms regarding river pollution to the State Environmental Inspectorate and local self-government bodies. You can download the application form at the link.






